Innovative Testing of High Reliability PCB Manufacturers
By Tim Estes, Lance Auer, Nick Meeker, and Mark Northrup
PCB’s (printed circuit boards) were first used in the 1920s. They were fabricated from materials known as Bakelite, Masonite, layered cardboard and even thin wooden (cellulose) planks. Holes were drilled into the fabricated PCB material. Flat brass “wires” were riveted or bolted onto the PCB. The electrical connections to mounted components were usually made by compressing the edge of a brass trace onto a hollow rivet. Subsequently, the process involved a component’s leads being pressed into the open end of the rivet. Even nuts and bolts were used in place of the rivets.

Mark Northrup
Single sided PCBs with laminates using different types of resins mixed with all sorts of different materials were introduced in the 1950s. Single sided required that the circuitry was on one side of the board and the components placed on the other. PCBs were much less bulky when compared to wiring and cables. Hence, the PCB made it a prime choice for new products being brought into the evolving electronics market place.
The government agencies responsible for the new weapons and communication equipment high reliability requirements resulted in their being the largest influence on the evolution of the printed circuit board. Wire ended components were being used in some of the applications. In the beginning the leads of the components were held in place on the board by using small nickel plates welded to the lead after it was placed through the hole!
Fast forward to today, and we are still trying to improve upon the printed circuit board to support government military, aerospace, and defense electronics high reliability needs. Electronics designs now require reduced sized conductors and spaces, multiple type vias (e.g., hole formation and registration), critical soldermask registration, controlled-depth drilling overshoot, and precise controlled impedance tolerances.
Enter the in 1994 CAT and the IPC-9151D Printed Board Process Capability and Relative Reliability (PCQR2) benchmark test standard and database to evaluate printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing processes. This was done in accordance with the National Technology Roadmap for Electronic Interconnection in 2000/2001.
To become a PCQR2 database supplier – according to IPC-9151D and the CAT initiative – a fabricator submits a set of process capability panels for testing, data analysis and database inclusion. IPC-9151D clearly outlines the steps to accomplish this. This extensive supply chain management tool was developed by IPC and Conductor Analysis Technologies, Inc. (CAT) for designers, purchasers, assemblers and manufacturers of printed boards. It’s based on statistical data (collected from industry-developed patterns) that quantify the quality, capability and reliability of printed board manufacturers.
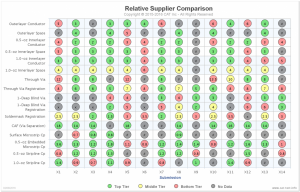
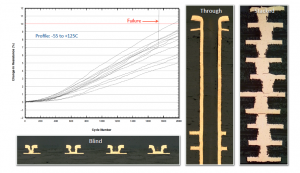
The purpose of the PCQR2 database is to strengthen supply chain management. It provides a detailed snapshot of supplier fabrication capabilities in five different areas: 1) conductors and spaces, 2) vias (e.g., hole formation and registration), 3) soldermask registration, 4) controlled-depth drilling overshoot, and 5) controlled impedance. It is a unique supply PCB supply chain management resource.
By evaluating two or more processes our analysis provides the data necessary for comparison and selection. This allows users of printed circuit boards to:
- Benchmark your board suppliers’ capabilities
- Perform intelligent sourcing
- Select new suppliers
- Ensure design for manufacturability
- Establish realistic design rules
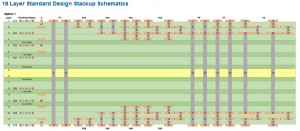
This capability test consists of three builds of five panels each over a several week period. The Test Board Panel Designs which is created by CAT, consists of a defined board layer count (e.g., 8-24 layers), with blind /buried/micro vias combinations, scaled traces / spaces, and aspect ratio holes. CAT applies PCQR2 to help provide a peer comparison of process capability along with establishing a baseline for on-going enhancements to strengthen the company’s performance and relative results among your supply chain PCB manufacturers. Conductor Analysis Technologies, Inc. (CAT) solely manages the ability to perform this comparison of printed circuit board fabricators manufacturing aspects and capabilities
Currently the following companies are PCQR2 Program Subscribers
- BAE Systems
- Bose Corporation
- Dell Inc.
- Harris Corporation
- Hella GmbH
- Honeywell International Inc.
- IEC Electronics Corporation
- Intel Corporation
- MIT Lincoln Laboratory
- National Instruments Corporation
- NSWC Crane
- Raytheon Company
- Sandia National Laboratories
In 2017 Conductor Analysis Technologies, Inc. (CAT) released a new IPC Process Capability, Quality and Reliability (PCQR2) set of test patterns. The patterns were developed by CAT with guidance from the IPC-D36 subcommittee and are used by OEMs. The new patterns are available in 8-, 10-, 12-, 18-, and 24 -layer designs and provide more insight into complex microvia structures, including stacked and staggered, than previous designs. Additionally, the new patterns require only 12 panels to be manufactured per submission, a 20% reduction.
Mark Northrup is an EMSNOW Contributor. Nick Meeker, Lance Auer and Tim Estes are with CAT.