CoWoS Capacity Shortage Challenges AI Chip Demand, while Taiwanese Manufacturers Expand to Seize Opportunities
With the flourishing development of technologies such as AI, cloud computing, big data analytics, and mobile computing, modern society has an increasingly high demand for computing power.
Moreover, with the advancement beyond 3 nanometers, wafer sizes have encountered scaling limitations and manufacturing costs have increased. Therefore, besides continuing to develop advanced processes, the semiconductor industry is also exploring other ways to maintain chip size while ensuring high efficiency.
The concept of “heterogeneous integration” has become a contemporary focus, leading to the transition of chips from single-layer to advanced packaging with multiple layers stacked together.
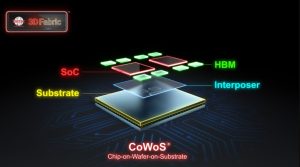
The term “CoWoS” can be broken down into the following definitions: “Cow” stands for “Chip-on-Wafer,” referring to the stacking of chips, while “WoS” stands for “Wafer-on-Substrate,” which involves stacking chips on a substrate.
Therefore, “CoWoS” collectively refers to stacking chips and packaging them onto a substrate. This approach reduces the space required for chips and offers benefits in reducing power consumption and costs.
Among these, CoWoS can be further divided into 2.5D horizontal stacking (most famously exemplified by TSMC’s CoWoS) and 3D vertical stacking versions. In these configurations, various processor and memory modules are stacked layer by layer to create chiplets. Because its primary application lies in advanced processes, it is also referred to as advanced packaging.
According to TrendForce’s data, it has provided insights into the heat of the AI chip market. In 2023, shipments of AI servers (including those equipped with GPU, FPGA, ASIC, etc.) reached nearly 1.2 million units, a 38.4% increase from 2022, accounting for nearly 9% of the overall server shipments.
Looking ahead to 2026, the proportion is expected to reach 15%, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of AI server shipments from 2022 to 2026 reaching 22%.
Due to the advanced packaging requirements of AI chips, TSMC’s 2.5D advanced packaging CoWoS technology is currently the primary technology used for AI chips.
GPUs, in particular, utilize higher specifications of HBM, which require the integration of core dies using 2.5D advanced packaging technology. The initial stage of chip stacking in CoWoS packaging, known as Chip on Wafer (CoW), primarily undergoes manufacturing at the fab using a 65-nanometer process. Following this, through-silicon via (TSV) is carried out, and the finalized products are stacked and packaged onto the substrate, known as Wafer on Substrate (WoS).
As a result, the production capacity of CoWoS packaging technology has become a significant bottleneck in AI chip output over the past year, and it remains a key factor in whether AI chip demand can be met in 2024. Foreign analysts have previously pointed out that NVIDIA is currently the largest customer of TSMC’s 2.5D advanced packaging CoWoS technology.
This includes NVIDIA’s H100 GPU, which utilizes TSMC’s 4-nanometer advanced process, as well as the A100 GPU, which uses TSMC’s 7-nanometer process, both of which are packaged using CoWoS technology. As a result, NVIDIA’s chips account for 40% to 50% of TSMC’s CoWoS packaging capacity. This is also why the high demand for NVIDIA chips has led to tight capacity for TSMC’s CoWoS packaging.
TSMC’s Expansion Plans Expected to Ease Tight Supply Situation in 2024
During the earnings call held in July 2023, TSMC announced its plans to double the CoWoS capacity, indicating that the supply-demand imbalance in the market could be alleviated by the end of 2024.
Subsequently, in late July 2023, TSMC announced an investment of nearly NTD 90 billion (roughly USD 2.87 billion) to establish an advanced packaging fab in the Tongluo Science Park, with the construction expected to be completed by the end of 2026 and mass production scheduled for the second or third quarter of 2027.
In addition, during the earnings call on January 18, 2024, TSMC’s CFO, Wendell Huang, emphasized that TSMC would continue its expansion of advanced processes in 2024. Therefore, it is estimated that 10% of the total capital expenditure for the year will be allocated towards expanding capacity in advanced packaging, testing, photomasks, and other areas.
In fact, NVIDIA’s CFO, Colette Kress, stated during an investor conference that the key process of CoWoS advanced packaging has been developed and certified with other suppliers. Kress further anticipated that supply would gradually increase over the coming quarters.
Regarding this, J.P. Morgan, an investment firm, pointed out that the bottleneck in CoWoS capacity is primarily due to the supply-demand gap in the interposer. This is because the TSV process is complex, and expanding capacity requires more high-precision equipment. However, the long lead time for high-precision equipment, coupled with the need for regular cleaning and inspection of existing equipment, has resulted in supply shortages.
Apart from TSMC’s dominance in the CoWoS advanced packaging market, other Taiwanese companies such as UMC, ASE Technology Holding, and Powertek Technology are also gradually entering the CoWoS advanced packaging market.
Among them, UMC expressed during an investor conference in late July 2023 that it is accelerating the deployment of silicon interposer technology and capacity to meet customer needs in the 2.5D advanced packaging sector.
UMC Expands Interposer Capacity; ASE Pushes Forward with VIPack Advanced Packaging Platform
UMC emphasizes that it is the world’s first foundry to offer an open system solution for silicon interposer manufacturing. Through this open system collaboration (UMC+OSAT), UMC can provide a fully validated supply chain for rapid mass production implementation.
On the other hand, in terms of shipment volume, ASE Group currently holds approximately a 32% market share in the global Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test (OSAT) industry and accounts for over 50% of the OSAT shipment volume in Taiwan. Its subsidiary, ASE Semiconductor, also notes the recent focus on CoWoS packaging technology. ASE Group has been strategically positioning itself in advanced packaging, working closely with TSMC as a key partner.
ASE underscores the significance of its VIPack advanced packaging platform, designed to provide vertical interconnect integration solutions. VIPack represents the next generation of 3D heterogeneous integration architecture.
Leveraging advanced redistribution layer (RDL) processes, embedded integration, and 2.5D/3D packaging technologies, VIPack enables customers to integrate multiple chips into a single package, unlocking unprecedented innovation in various applications.
Powertech Technology Seeks Collaboration with Foundries; Winbond Electronics Offers Heterogeneous Integration Packaging Technology
In addition, the OSAT player Powertech Technology is actively expanding its presence in advanced packaging for logic chips and AI applications.
The collaboration between Powertech and Winbond is expected to offer customers various options for CoWoS advanced packaging, indicating that CoWoS-related advanced packaging products could be available as early as the second half of 2024.
Winbond Electronics emphasizes that the collaboration project will involve Winbond Electronics providing CUBE (Customized Ultra-High Bandwidth Element) DRAM, as well as customized silicon interposers and integrated decoupling capacitors, among other advanced technologies. These will be complemented by Powertech Technology’s 2.5D and 3D packaging services.